Antimony: A Critical Element in the Contemporary Technological Landscape

By Staff Writer
Antimony, a metalloid situated in the nitrogen group of the periodic table, distinguishes itself through its unique properties, making it an invaluable resource in a myriad of industrial applications. Its primary manifestation, antimony trioxide, serves as a critical flame retardant, imbuing materials such as plastics, textiles, and electronic devices with essential safety features. The significance of antimony extends far beyond this primary use, permeating various sectors and highlighting its versatile nature.

In the realm of electrochemical applications, antimony is indispensable in enhancing the mechanical strength and charging characteristics of lead-acid batteries. These batteries play a crucial role in automotive and stationary storage applications, where reliability and efficiency are paramount. Furthermore, antimony’s ability to alloy with lead and other metals to improve hardness and mechanical robustness is leveraged in the production of projectiles, electrical cable sheathing, and type metal for high-resolution printing processes. This metallurgical innovation underscores the element’s pivotal role in modern manufacturing and technology.
The chemical industry also benefits from the unique properties of antimony compounds, which serve as catalysts in the manufacturing of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) polymers. These polymers are essential in the production of various consumer goods, ranging from beverage containers to clothing. Additionally, antimony’s catalytic properties are exploited in the synthesis of certain plastics and chemicals, further illustrating its critical role in contemporary industrial processes.
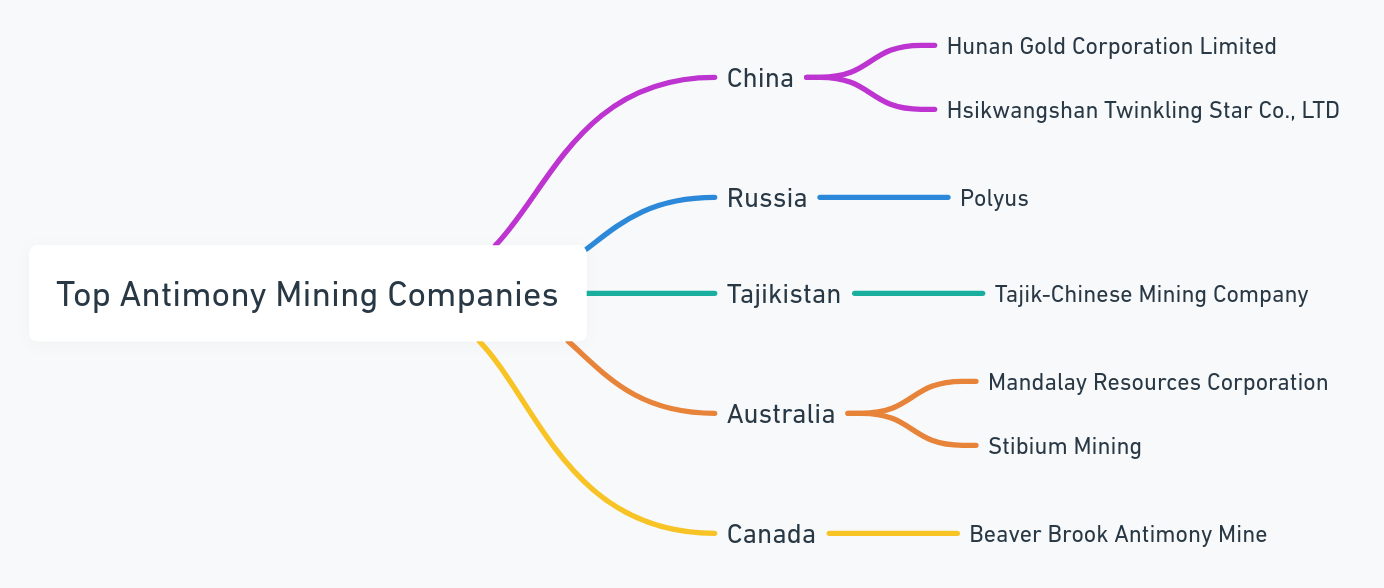 The global extraction of antimony is a complex endeavor, with China leading the world in production, followed by Russia, Bolivia, and Tajikistan. The Stibnite Mine in Idaho, USA, represents a significant North American operation, indicating efforts to diversify the global supply chain of this critical mineral. Companies such as Hunan Gold Corporation Limited in China and the United States Antimony Corporation (USAC) are at the forefront of this industry, engaging in the mining, processing, and smelting of antimony. Their activities ensure the steady flow of antimony to meet global demand, highlighting the strategic importance of this element in the international market.
The global extraction of antimony is a complex endeavor, with China leading the world in production, followed by Russia, Bolivia, and Tajikistan. The Stibnite Mine in Idaho, USA, represents a significant North American operation, indicating efforts to diversify the global supply chain of this critical mineral. Companies such as Hunan Gold Corporation Limited in China and the United States Antimony Corporation (USAC) are at the forefront of this industry, engaging in the mining, processing, and smelting of antimony. Their activities ensure the steady flow of antimony to meet global demand, highlighting the strategic importance of this element in the international market.
The processing of antimony ore is a detailed and sophisticated process that involves crushing, grinding, flotation, and sometimes roasting and smelting to produce antimony metal or antimony trioxide. This process is tailored to the characteristics of the ore and the requirements of the end product, aiming for the highest possible purity and specific form desired for industrial use.
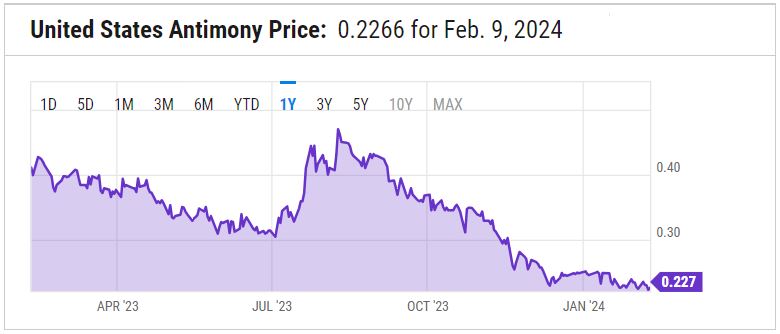 As the demand for antimony continues to grow, driven by its applications in flame retardants, lead-acid batteries, and emerging technologies such as microelectronics and photovoltaic materials, the industry faces the challenge of balancing economic growth with environmental stewardship and health safety. This necessitates ongoing innovation in mining technologies and processing methods, as well as the implementation of rigorous regulatory standards to mitigate the environmental impact of antimony production.
As the demand for antimony continues to grow, driven by its applications in flame retardants, lead-acid batteries, and emerging technologies such as microelectronics and photovoltaic materials, the industry faces the challenge of balancing economic growth with environmental stewardship and health safety. This necessitates ongoing innovation in mining technologies and processing methods, as well as the implementation of rigorous regulatory standards to mitigate the environmental impact of antimony production.
Antimony’s role in modern industry cannot be overstated, with its diverse applications underscoring its critical importance. The future of antimony production hinges on sustainable practices, recycling, and the development of alternative materials, which will be essential in reducing the environmental footprint of this invaluable element. As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, the antimony industry must navigate the complexities of economic development, environmental protection, and health safety to continue its contribution to global technological advancement.
